
Risk no longer lives in silos. When security teams identify a cybersecurity threat, it impacts regulatory compliance. When compliance finds a gap, it affects audit findings. When environmental, social and governance (ESG) initiatives encounter challenges, they create financial and reputational risks across the enterprise.
Organizations with disconnected risk functions face a dangerous reality: Risk information scattered across departments means leadership lacks visibility into how threats compound across the business.
According to PwC’s Global Compliance Survey, only 7% of organizations currently consider themselves leading in compliance maturity, with just 31% classifying themselves as mature, leaving most vulnerable to blind spots that regulatory bodies and stakeholders increasingly scrutinize.
To address these gaps, Integrated risk management (IRM) creates a unified view of enterprise risk by connecting internal audit, compliance, security, risk management and ESG functions on a single platform. This approach transforms risk from reactive firefighting into proactive business intelligence that supports strategic decision-making across all organizational levels.
This detailed guide explains:
Integrated risk management (IRM) is a holistic practice that creates a single view of risk on a unified platform across internal audit, internal controls, compliance, risk management and ESG teams. Rather than managing risks in departmental silos, IRM connects risk data, processes, and insights to provide leadership with unified visibility into enterprise threats and opportunities.
Research firm Gartner, which first coined the term "integrated risk management" in 2017, defines IRM as "a set of practices and processes supported by a risk-aware culture and enabling technologies." This definition emphasizes that successful IRM requires both organizational culture and the right technological infrastructure.
Organizations previously managed risk through separate teams handling cybersecurity, operational risk, compliance, and audit functions. Today's regulatory complexity and interconnected risks make this siloed approach both inefficient and dangerous.
"Risks are all integrated; they're not isolated," says Edna Conway, Board Director and Executive Advisor. This reality drives the need for integrated risk management approaches that reflect how risks actually compound across modern organizations.
Integrated risk management is important because technology is changing faster today than ever, bringing with it new risks relating to digital technology and cybersecurity. IRM helps your organization keep pace with this challenge.
In many organizations, the chief executive officer (CEO) and executive board, rather than regulatory bodies, are now in control of risk management. Regulatory bodies pushing these executives to adopt best practices worked well in the past; siloed teams were acceptable for managing risk programs when new technology options were few. Having separate security and risk management teams worked to achieve the organization’s goals.
With new risks and new regulatory requirements continuously evolving, these strategies no longer work. Modern organizations require new governance and risk management solutions that allow for complete oversight rather than siloed teams with a limited understanding of how they connect. This is why integrated risk management is important to your overall GRC strategy.
"There needs to be collaboration between risk and the business, vertically up and down, but then also horizontally across the organization," says Michael Rasmussen, CEO of GRC Report. "The problem is there are silos."
Taking action toward the six elements of integrated risk management can help jumpstart your journey toward a more comprehensive risk strategy. According to Gartner, IRM has the following characteristics:
Moving from siloed risk management to true integration requires systematic change across people, processes, and technology. Organizations successfully implementing IRM typically follow this progression:
IRM requires organizational change that only executive leadership can authorize. Chief risk officers, chief audit executives, chief compliance officers and chief information security officers must align on shared objectives, agree on integration priorities and commit resources to the initiative.
Create a steering committee with representation from all risk functions. This team defines the IRM vision, establishes governance structures and resolves conflicts between departmental priorities and enterprise integration needs.
Different risk functions often use different terminologies to describe similar concepts. Security teams discuss "vulnerabilities," while compliance teams reference "control gaps," and risk managers identify "exposures."
Develop an enterprise risk taxonomy that all teams adopt, standardize risk rating methodologies so assessment results can be compared across functions, and create unified risk categories that map to business objectives rather than departmental structures.
Technology selection represents a critical decision point. Evaluate IRM platforms based on:
Organizations should prioritize platforms that offer both depth in risk capabilities and breadth across all GRC functions. Disconnected point solutions perpetuate silos even when marketed as "integrated."
Complete IRM transformation takes time. Start with integration initiatives that demonstrate clear value quickly. Common starting points include:
Track metrics that demonstrate IRM value. This includes a reduction in risk assessment cycle time, an increase in cross-functional risk identification, an improvement in board-level risk reporting satisfaction, a decrease in duplicate risk mitigation efforts and an acceleration in emerging risk response times.
Use early wins to build momentum for broader integration across all risk functions.
ESG factors represent critical risk domains that belong within integrated risk management frameworks rather than existing as separate initiatives. The question isn't whether ESG relates to IRM — it's how to ensure ESG risks receive the same rigorous oversight as financial, operational and compliance threats.
ESG factors create tangible business risks that cascade across organizations:
Organizations treating ESG as separate from core risk management create dangerous blind spots. Climate risk isn't just an environmental issue — it's a supply chain risk, a financial risk, a regulatory risk and potentially a reputation risk.
Additionally, social considerations affect operational continuity and legal exposure, and governance failures enable risks across all other domains.
Organizations implementing IRM should incorporate ESG through systematic integration across all core risk activities:
This approach ensures that ESG considerations inform strategic decisions rather than existing as compliance checkbox exercises that are disconnected from actual business risk management.
Selecting appropriate IRM technology requires understanding that integrated risk management tools are fundamental aspects of successful IRM adoption. Gartner's definition explicitly includes "enabling technologies" as core components of effective IRM frameworks.
IRM solutions should provide integrated risk management software that facilitates organizational transformation by automating risk data collection, implementing triggers and automated actions when risk thresholds are reached and providing comprehensive analytics for strategic decision making.
When considering an IRM solution, you should think about:
Organizations can no longer afford disconnected risk functions that create blind spots in enterprise oversight. Integrated risk management provides the unified visibility that boards, regulators and stakeholders increasingly demand.
With this in mind, Diligent provides a suite of integrated solutions. For example, the Diligent One Platform delivers IRM capabilities that connect audit, risk, compliance and ESG functions on a single unified platform.
Our AI-powered solutions accelerate risk identification, automate assessment workflows, and provide the strategic intelligence that transforms risk management from defensive compliance into proactive business value.
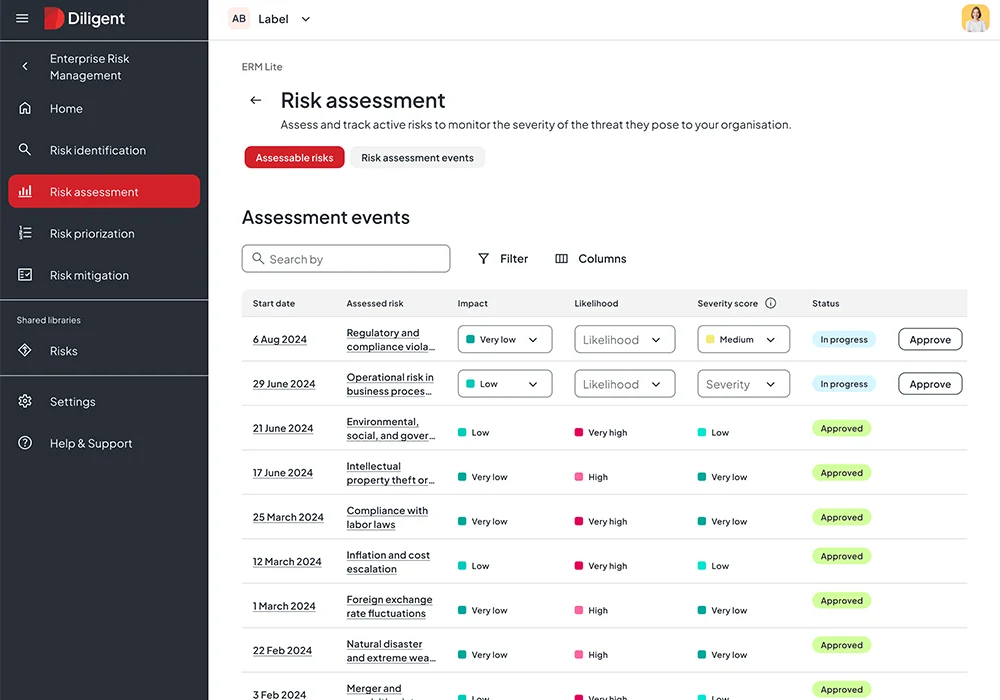
Built on this foundation, Diligent's Enterprise Risk Management solution enables organizations to strategically manage risk by rapidly identifying, prioritizing and responding to risks wherever they originate.
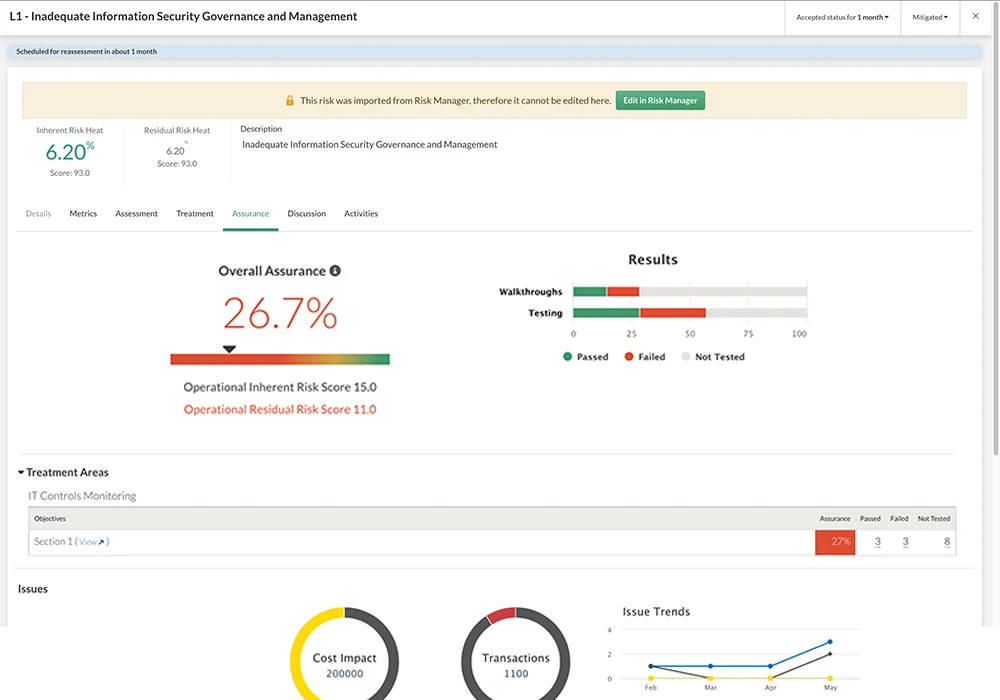
The platform provides complete visibility into enterprise risk posture with built-in dashboards and customizable reporting that empower executives to make confident, data-driven decisions. By automating manual workflows and eliminating departmental silos, organizations gain the holistic view needed to ensure audit-readiness and compliance across the enterprise.
Additionally, Diligent ACL Analytics provides the continuous monitoring and analytics capabilities that enable truly proactive risk management. Rather than periodic control testing, ACL Analytics monitors 100% of transaction data to identify anomalies and control failures the moment they occur.
Together, these solutions provide the integrated platform capabilities that mid-market and enterprise organizations need to mature from reactive risk management to proactive, intelligence-driven oversight.
Discover how Diligent's AI-powered IRM solutions can transform your risk management from siloed processes to enterprise-wide intelligence. Schedule a demo to see how we can help you achieve true integrated risk oversight.
GRC (governance, risk and compliance) is a broad organizational approach encompassing governance structures, risk management processes and regulatory compliance activities. IRM specifically focuses on integrating risk management functions across organizational silos to create unified risk visibility.
While GRC provides the framework, IRM represents the operational methodology for connecting previously separate risk functions.
Implementation timelines vary based on organizational complexity and integration scope. Organizations typically see value in three phases.
Most organizations see measurable benefits within the first 6 months, even while working toward complete transformation. Quick wins include: reduced time spent on risk assessments, improved board reporting satisfaction, better visibility into emerging threats, and elimination of duplicate mitigation efforts.
The primary challenge is cultural integration rather than technical implementation. Risk functions often resist integration, fearing loss of autonomy, while teams already at capacity struggle to dedicate time to adoption.
Technical obstacles include data quality issues when connecting siloed systems that use different terminologies, rating scales and documentation standards. Technology integration becomes complex when IRM platforms must connect with numerous existing business systems — making robust integration capabilities and pre-built connectors essential.
Success requires simultaneously aligning people, processes, data and technology around common operating models. Organizations should invest in change management, training and stakeholder engagement while planning for dedicated implementation resources rather than expecting adoption to happen alongside normal responsibilities.
Success metrics should focus on strategic outcomes rather than operational efficiency. Key indicators include: reduced time from risk identification to mitigation, improved board confidence in risk reporting, decreased regulatory compliance gaps and enhanced strategic decision-making speed.
AI transforms IRM from reactive to proactive through four key capabilities:
These capabilities accelerate response times, improve assessment accuracy and transform risk reporting from departmental updates into strategic business intelligence.
Ready to transform your risk management with AI-powered integration? Request a demo to see how Diligent can help your organization achieve true integrated risk management.